
An Accounting, Bookkeeping & Financial Analysis Engine for the Django Framework.#
Introducing Django Ledger, a powerful double entry accounting system designed for financially driven applications using the Django Web Framework. Developed by lead developer Miguel Sanda, this system offers a simplified, high-level API, making it easier for users to navigate the complexities of accounting. If you have prior experience with Django, you’ll find this software even more effective. And, for those interested in contributing, consider joining our new discord channel for further collaboration and discussions.
Questions? Join our Discord Channel Here#
Documentation#
Access the latest documentation and QuickStart guide here. Also, you may download the QuickStart Jupyter Notebook here.
Main Features#
High Level API.
Double entry accounting system.
Multiple Hierarchical Chart of Accounts.
Financial Statements (Income Statement, Balance Sheet & Cash Flow Statement).
Purchase Orders, Sales Orders (Estimates), Bills and Invoices.
Automatic financial ratio & insight calculations.
Multi tenancy (multiple companies/users/clients).
Self-contained Ledgers, Journal Entries & Transactions.
Basic OFX & QFX file import.
Closing Entries.
Items, lists & inventory management.
Unit of Measures.
Bank Accounts Information.
Django Admin Classes.
Built In Entity Management UI.
Need a new feature or report a bug?#
Feel free to initiate an Issue describing your new feature request.
Want to contribute?#
Finance and Accounting is a complicated subject. Django Ledger stands out from other Django projects due to its focus on providing a developer-friendly accounting engine and a reliable, extensible API for financially driven applications. The project requires expertise in Python, Django programming, finance, and accounting. In essence, the project is seeking assistance from individuals with the specific skill set needed to contribute effectively. So, it’s clear that they are in need of support from individuals with the right expertise.
The project is actively seeking contributors with financial and/or accounting experience. Prior accounting experience is a big plus for potential contributors. If you have the relevant experience and want to contribute, feel free to reach out to me. You can find the contribution guidelines at the specified link. The project welcomes anyone interested in making a contribution.
Installation#
Django Ledger is a Django application. If you haven’t, you need working knowledge of Django and a working Django project before you can use Django Ledger. A good place to start is here.
Make sure you refer to the django version you are using.
The easiest way to start is to use the zero-config Django Ledger starter template. See details here. Otherwise, you may create your project from scratch.
To create a new Django Ledger project:
Make sure you have the latest version of python here (recommended).
Install Django:
pip install django
Install Python Pipenv (python package manager):
pip install pipenv
Go to your desired development folder and create a new django project:
django-admin startproject django_ledger_project && cd django_ledger_project
Install Django on you virtual environment.
pipenv install django
Install Django Ledger
pipenv install django-ledger[graphql,pdf]
Activate your new virtual environment:
pipenv shell
Add django_ledger to INSTALLED_APPS in you new Django Project.
INSTALLED_APPS = [
...,
'django_ledger',
...,
]
Perform database migrations:
python manage.py migrate
Add Django SuperUser and follow the prompts.
python manage.py createsuperuser
Add URLs to your project’s urls.py:
from django.urls import include, path
urlpatterns = [
...,
path('ledger/', include('django_ledger.urls', namespace='django_ledger')),
...,
]
Run your project:
python manage.py runserver
Navigate to Django Ledger root view assigned in your project urlpatterns setting ( typically http://127.0.0.1:8000/ledger if you followed this installation guide).
Use your superuser credentials to login.
How To Set Up Django Ledger for Development#
Django Ledger comes with a basic development environment already configured under dev_env/ folder not to be used for production environments. If you want to contribute to the project perform the following steps:
Navigate to your projects directory.
Clone the repo from github and CD into project.
git clone https://github.com/arrobalytics/django-ledger.git && cd django-ledger
Install PipEnv, if not already installed:
pip install -U pipenv
Create virtual environment.
pipenv install
If using a specific version of Python you may specify the path.
pipenv install --python PATH_TO_INTERPRETER
Activate environment.
pipenv shell
Apply migrations.
python manage.py migrate
Create a Development Django user.
python manage.py createsuperuser
Run development server.
python manage.py runserver
How To Set Up Django Ledger for Development using Docker#
Navigate to your projects directory.
Give executable permissions to entrypoint.sh
sudo chmod +x entrypoint.sh
Add host ‘0.0.0.0’ into ALLOWED_HOSTS in settings.py.
Build the image and run the container.
docker compose up --build
Add Django Superuser by running command in seprate terminal
docker ps
Select container id of running container and execute following command
docker exec -it containerId /bin/sh
python manage.py createsuperuser
Navigate to http://0.0.0.0:8000/ on browser.
Run Test Suite#
After setting up your development environment you may run tests.
python manage.py test django_ledger
Screenshots#

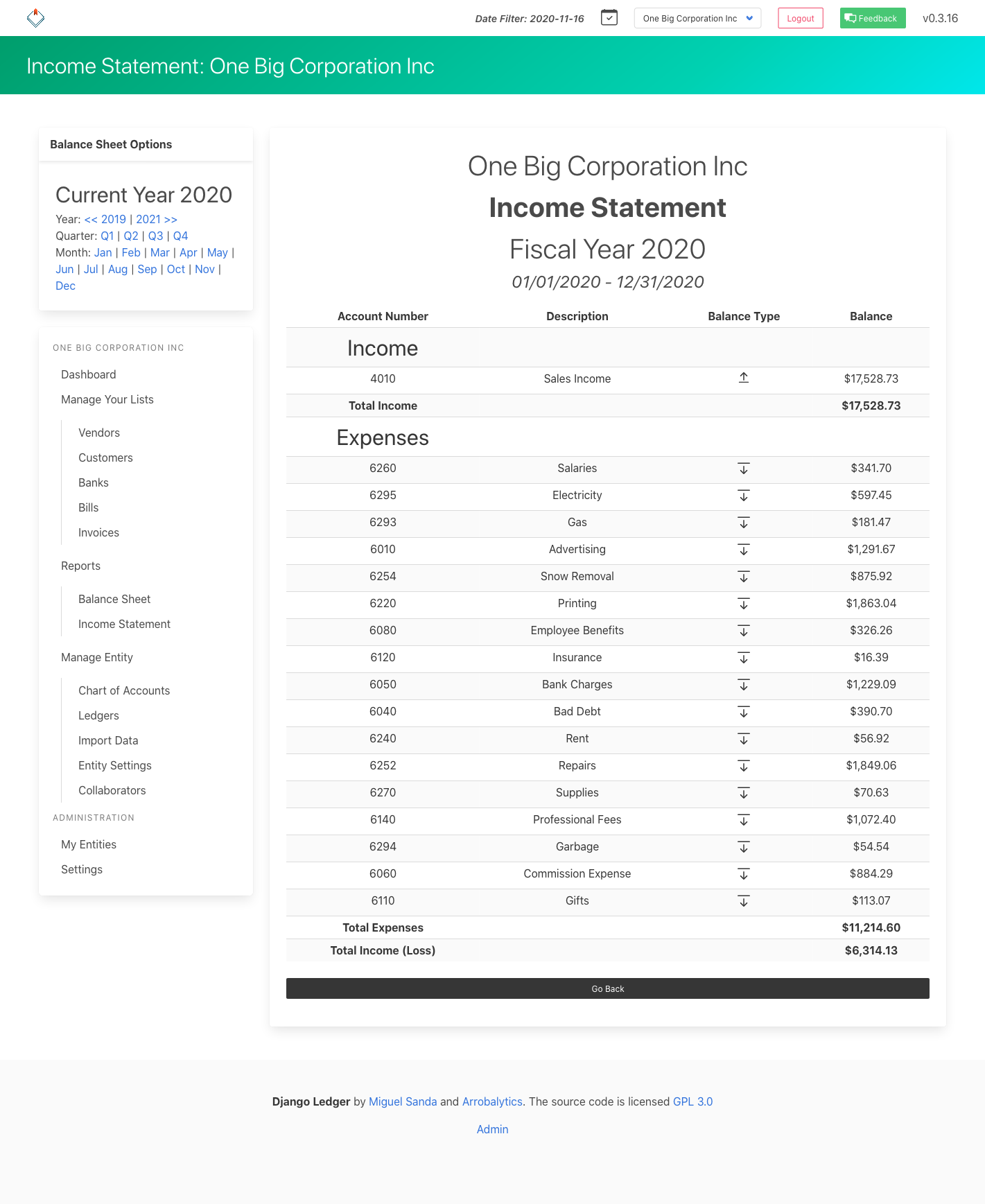
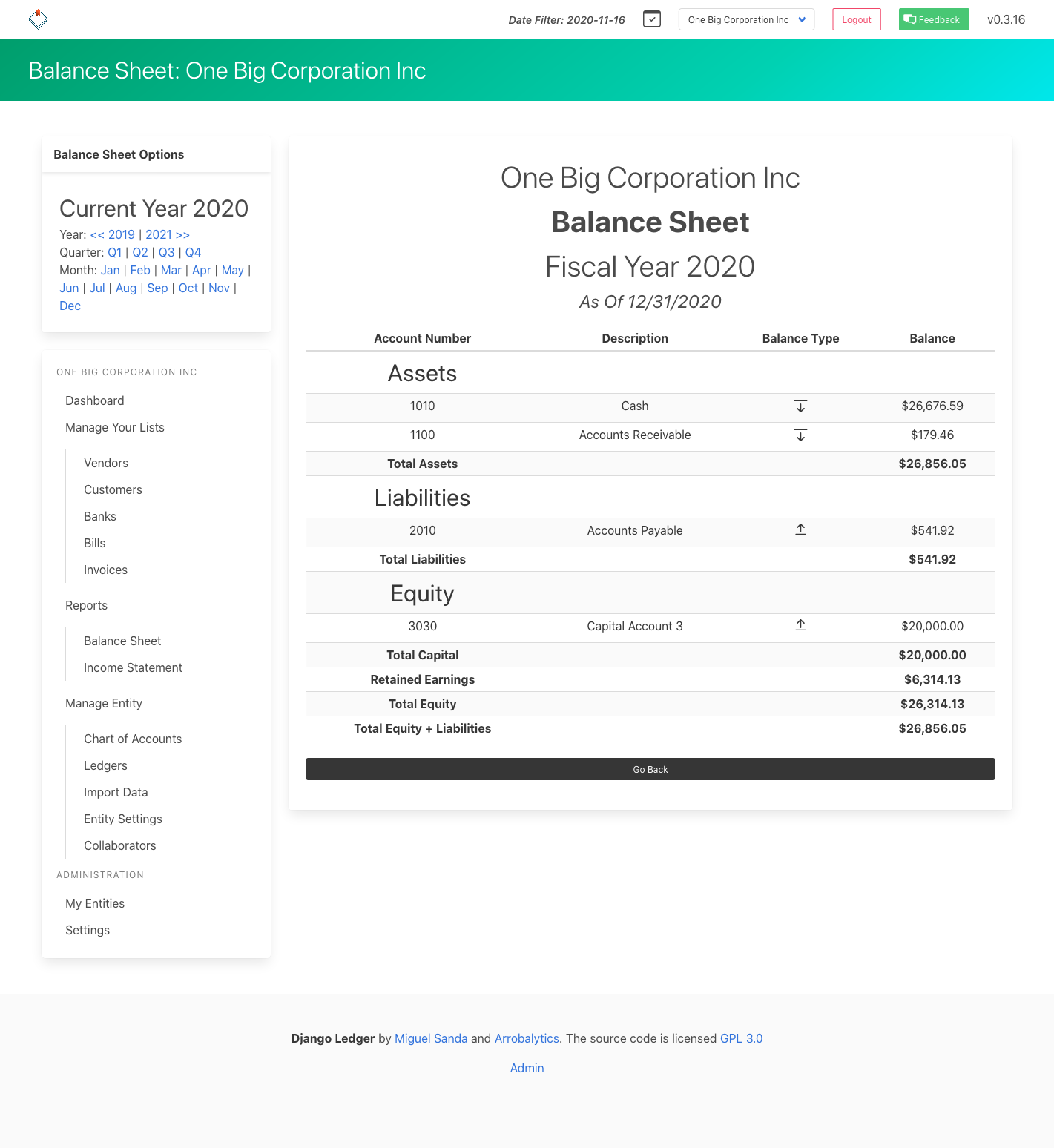


Financial Statements Screenshots#


